
#Summarize in r how to#
✏️ Integrated Color Coding - Color coding strategy encourages students to learn how to find and use text evidence in their answers. ⭐️Includes Lexile leveled passages, standard based questions, anchor charts, and hands-on cut-and-paste visuals to help students master this skill. This packet is designed to specifically fit 3rd grade Florida B.E.S.T standard ELA.3.R.3.2 but can be used by anyone teaching summarize in nonfiction. Summarizing is a brief account of the major events in a story. Our resulting tibble has 6 rows corresponding to the six combinations of species and sex values.⭐️These Lexile® leveled close reading stories are perfect for teaching students how to summarize in nonfiction. In the example below, we groupby() on species and sex and compute two summary stats for each combination of species and sex values. We can also use groupby() on multiple variables and use summarize() on multiple varaibles.

# species ave_flipper_length_mm ave_body_mass_g Summarize(ave_flipper_length_mm=mean(flipper_length_mm), In this example, we groupby() species variable and compute two summary statistics, mean flipper length and body mass. We can also use groupby() on single variable and do computation on multiple variables. Groupby() with single variable and multiple summary stats In our example, we have got mean bill length for each values of sex. Summarize(ave_bill_length_mm=mean(bill_length_mm)) Then when we use summarize() function it computes some summary statistics on each smaller dataframe and gives us a new dataframe. When we use groupby() function, in this example on a single variable, under the hood it splits the dataframe into multiple smaller dataframes such that there is a smaller dataframe for each value of the variable we used with groupby.įor example, when we use groupby() function on sex variable with two values Male and Female, groupby() function splits the original dataframe into two smaller dataframes one for “Male and the other for “Female”. Let us first use groupby() on a single variable in our dataframe. # species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm flipper_length_… body_mass_g sex We will use our favorite fantastic Penguins dataset to illustrate groupby and summary() functions. Let us get started by loading tidyverse, suite of R packages from RStudio. , And then we will learn how to compute multiple summary values.

And in this tidyverse tutorial, we will learn how to use dplyr’s groupby() and summarise() functions to group the data frame by one or more variables and compute one or more summary statistics using summarise() function.įirst we will start with how to group a dataframe by a single variable and compute one summary level statistics. Group By operation is at the heart of this useful data analysis strategy. Many data analysis problems involve the application of a split-apply-combine strategy, where you break up a big problem into manageable pieces, operate on each piece independently and then put all the pieces back together.Ĭheck out the original paper introducing the strategy by Hadley Wickham and it is a must read.
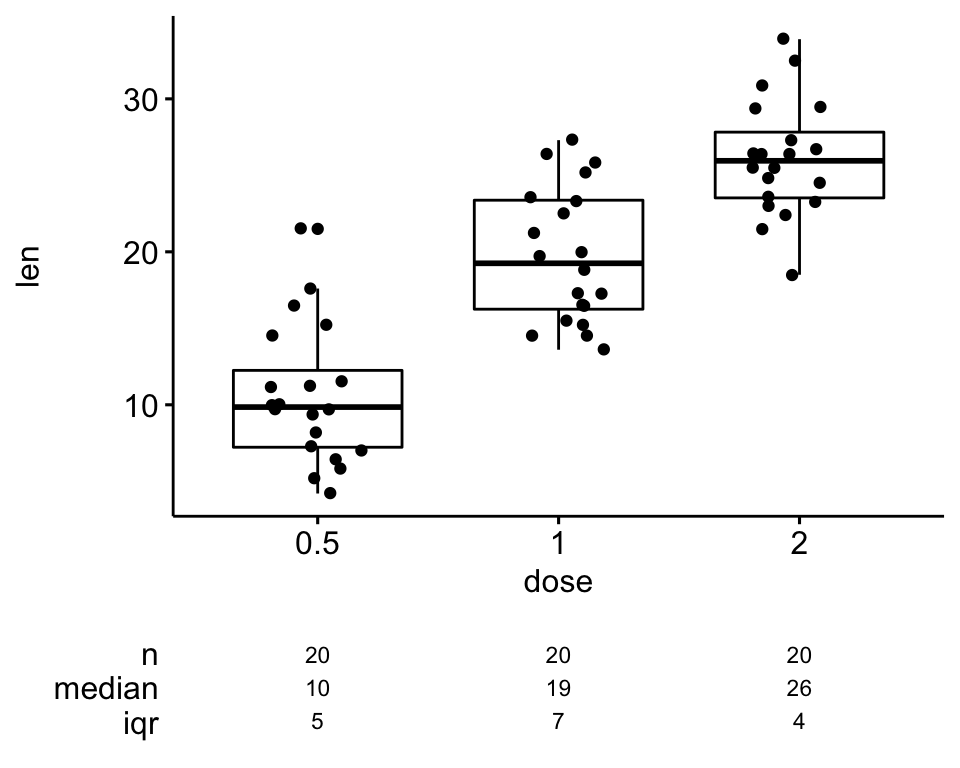
dplyr has a set of core functions for “data munging”,including select(),mutate(), filter(), groupby() & summarise(), and arrange().ĭplyr’s groupby() function is the at the core of Hadley Wickham’ Split-Apply-Combine paradigm useful for most common data analysis. Dplyr, is a R package provides that provides a great set of tools to manipulate datasets in the tabular form.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
